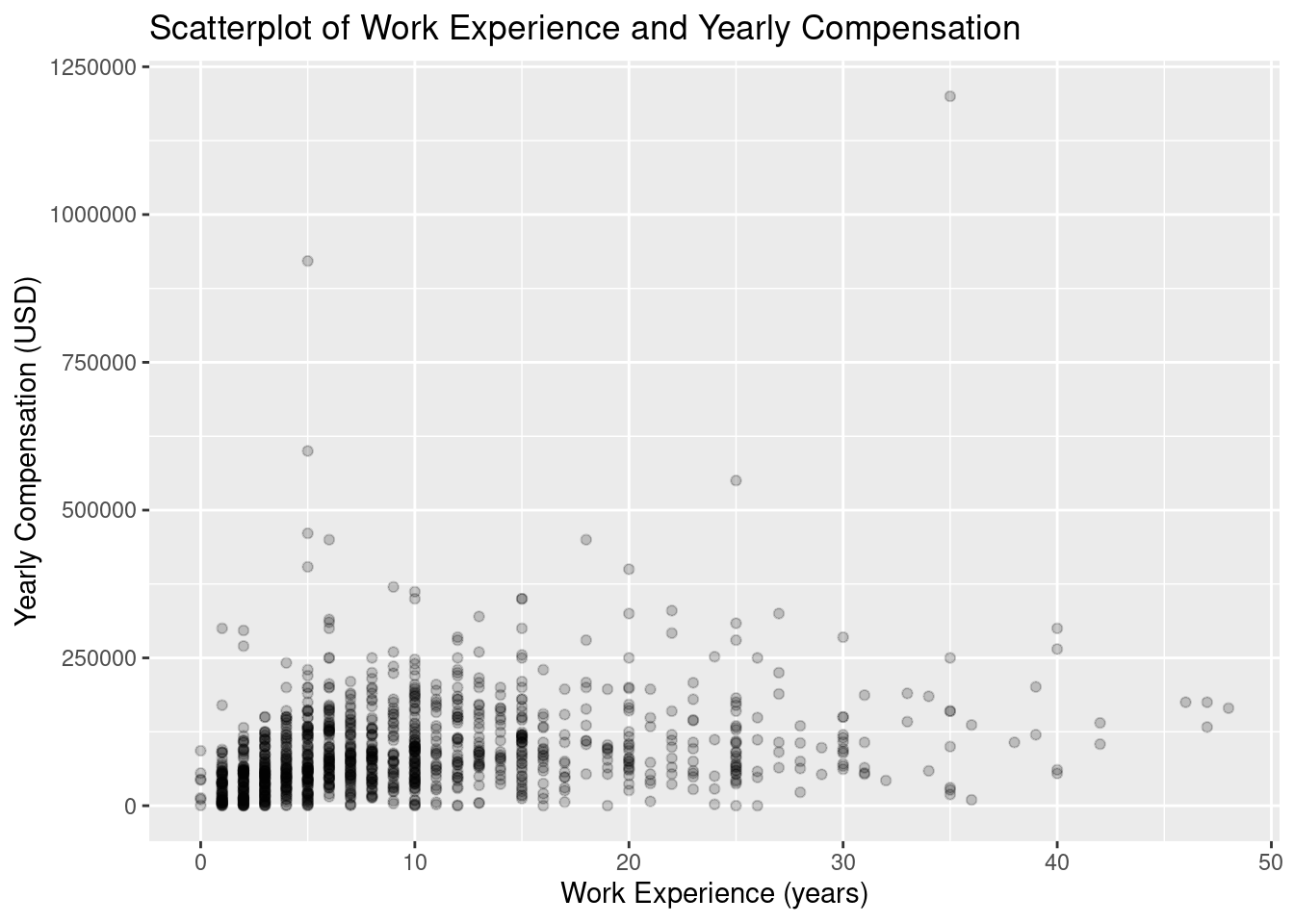
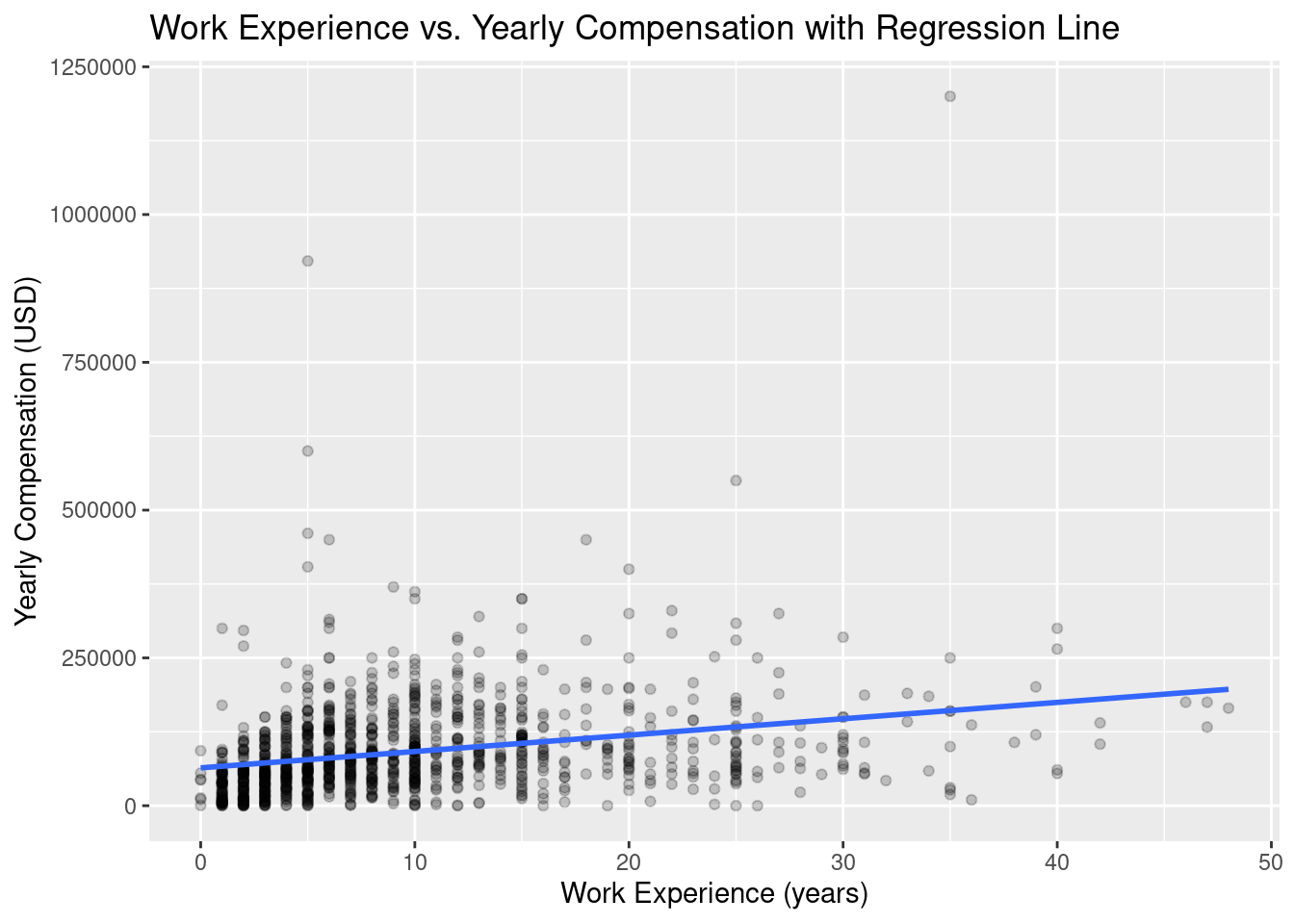
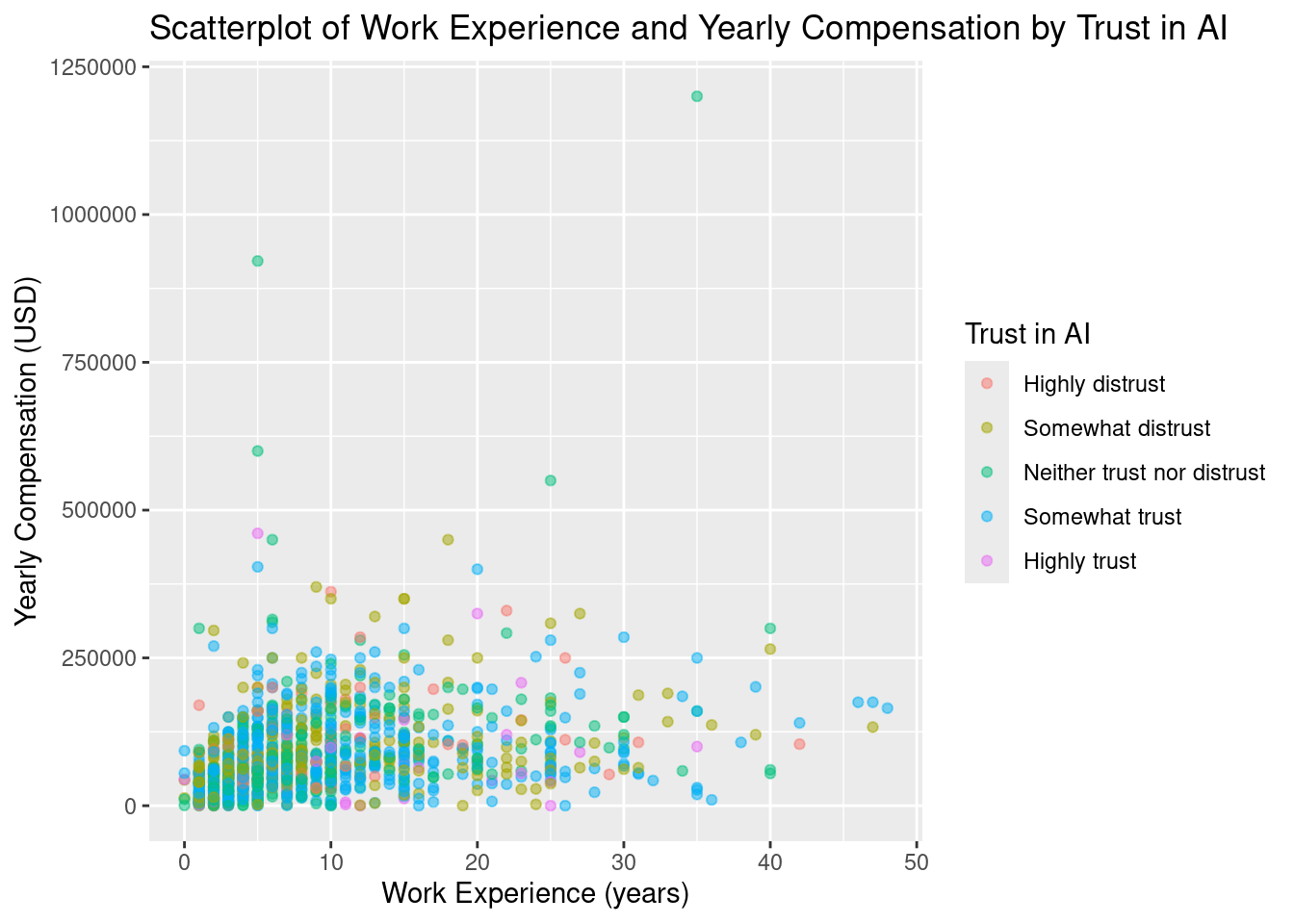
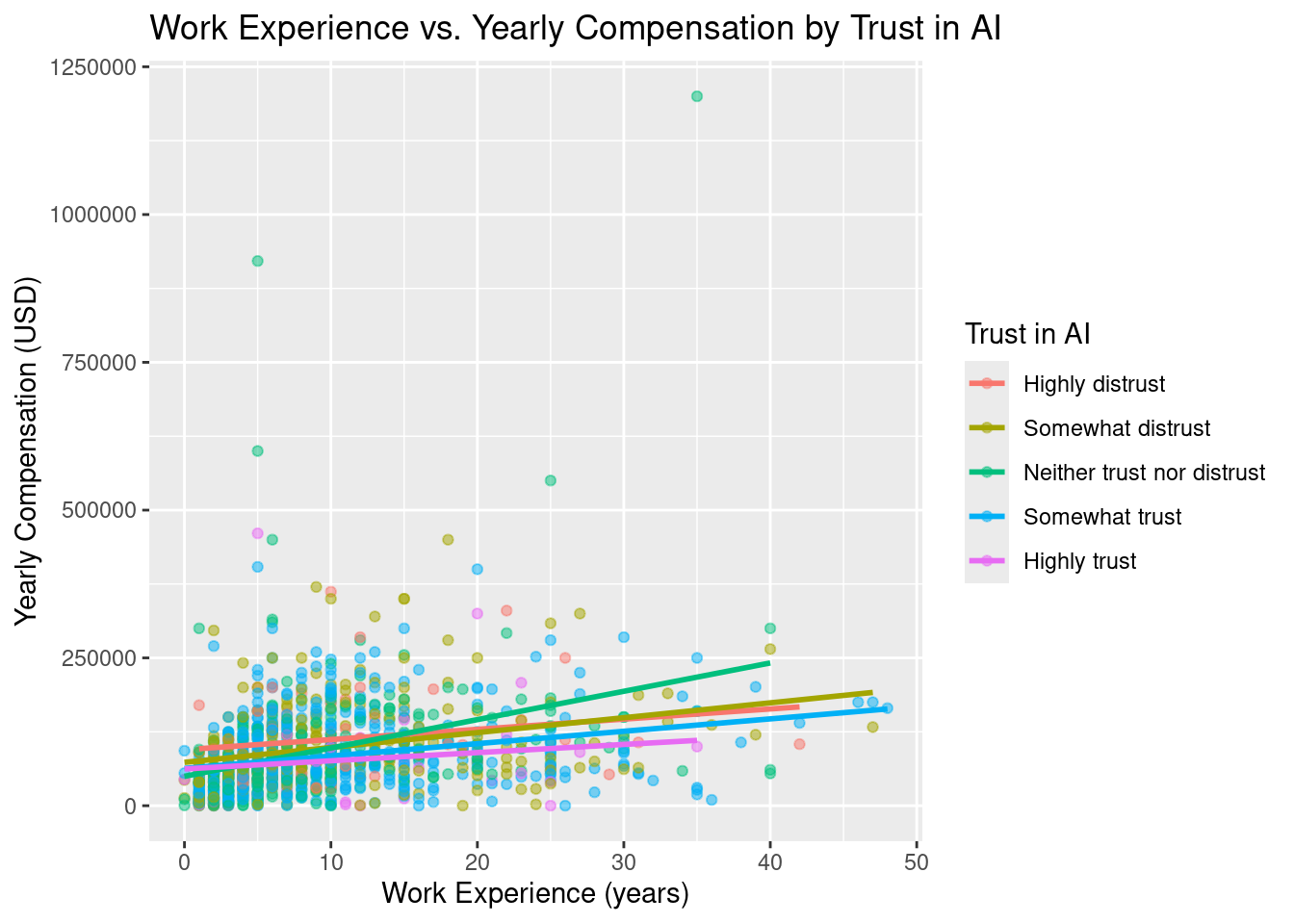
Rows: 1,182
Columns: 5
$ response_id <dbl> 164, 165, 190, 218, 220, 462, 542, 558, 577, 802, 815, 885, 1099, 1187, 1210, 1212, 1223…
$ converted_comp_yearly <dbl> 3237, 52046, 74963, 56757, 74963, 132260, 117798, 165974, 64254, 71779, 36351, 81349, 10…
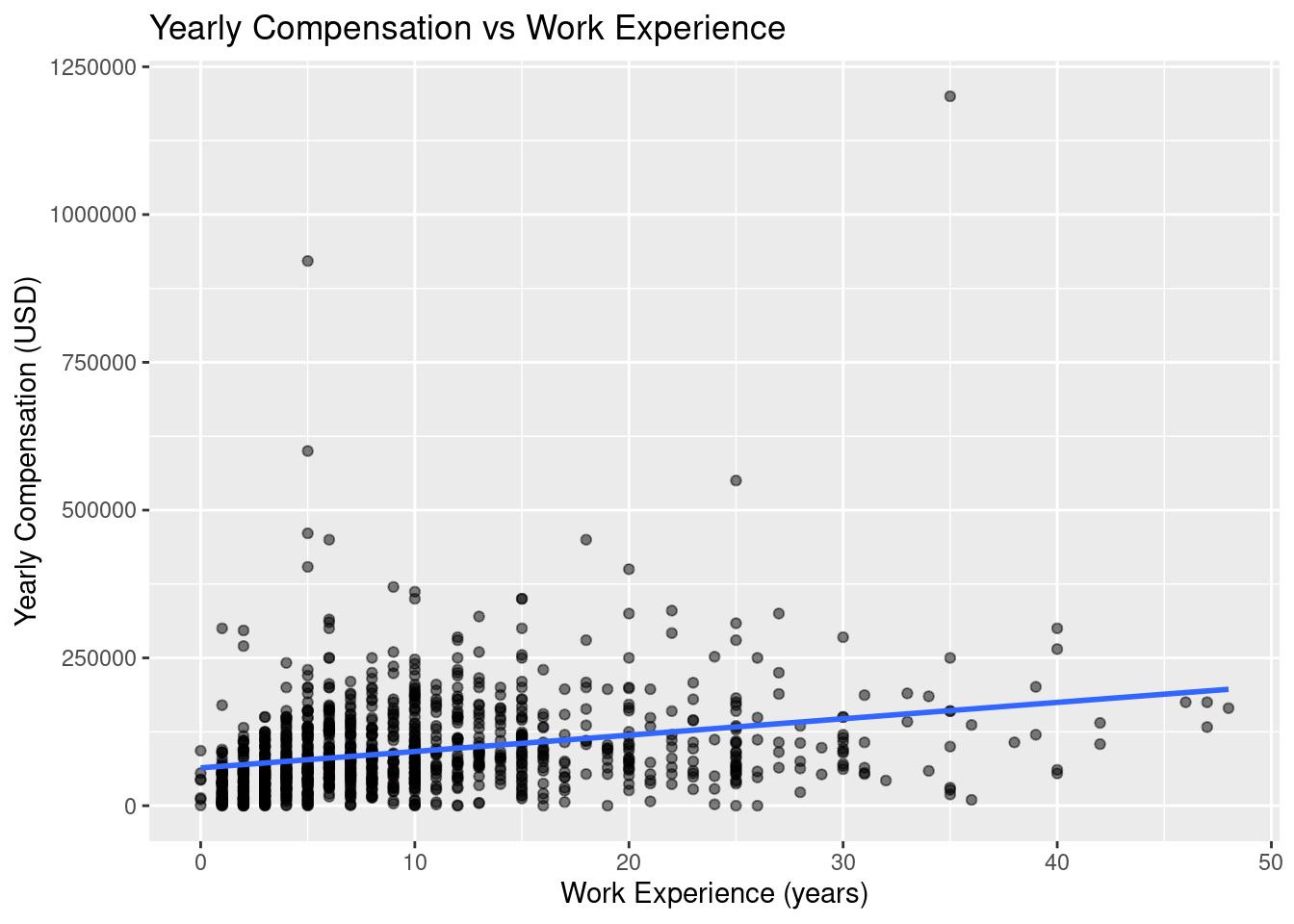
$ work_exp <dbl> 10, 7, 16, 17, 7, 25, 3, 7, 13, 10, 10, 13, 10, 19, 3, 14, 3, 5, 5, 2, 25, 30, 11, 2, 3,…
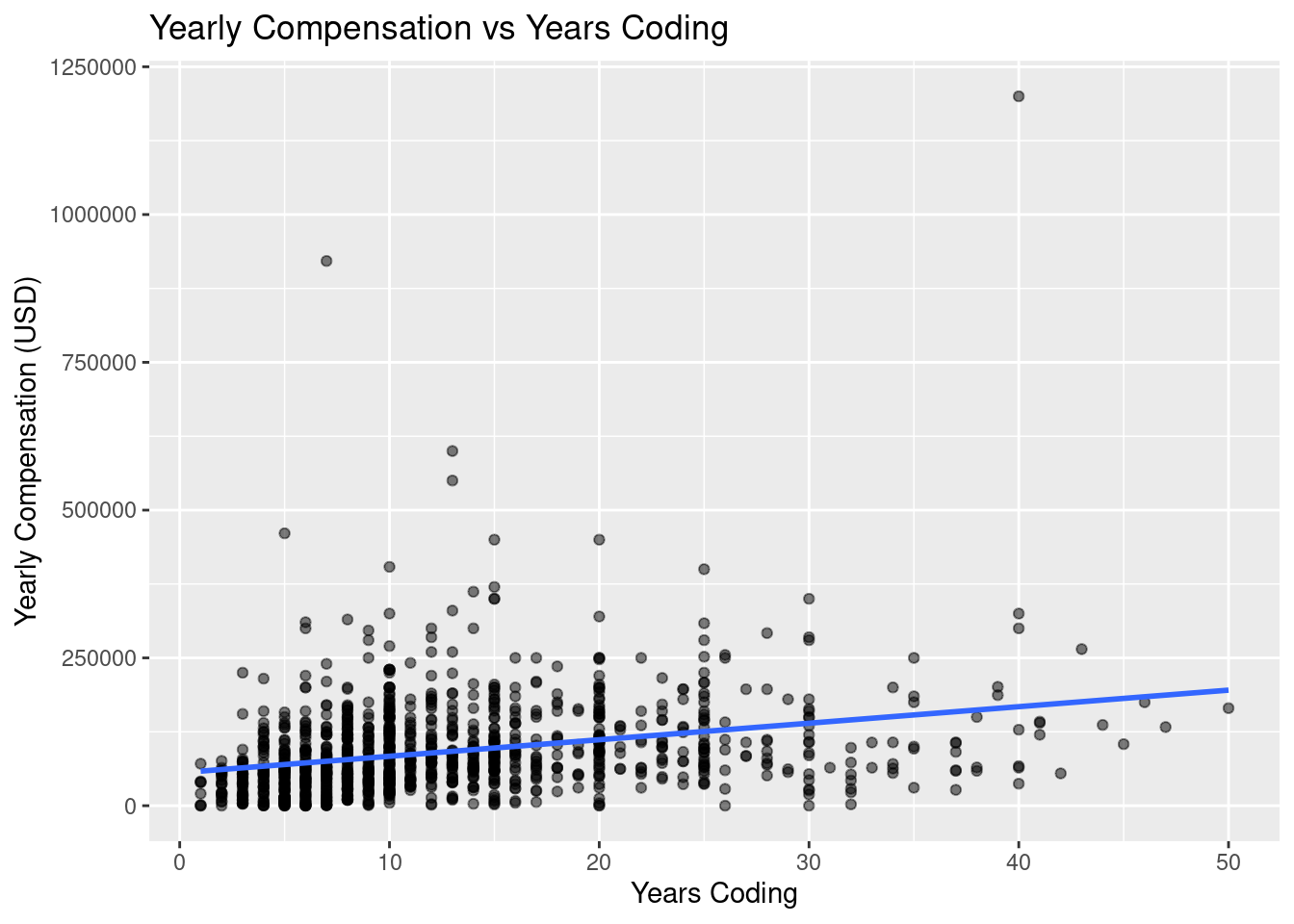
$ years_code <dbl> 14, 7, 8, 29, 7, 25, 13, 8, 22, 10, 3, 13, 8, 19, 3, 3, 7, 10, 15, 7, 27, 40, 15, 4, 7, …
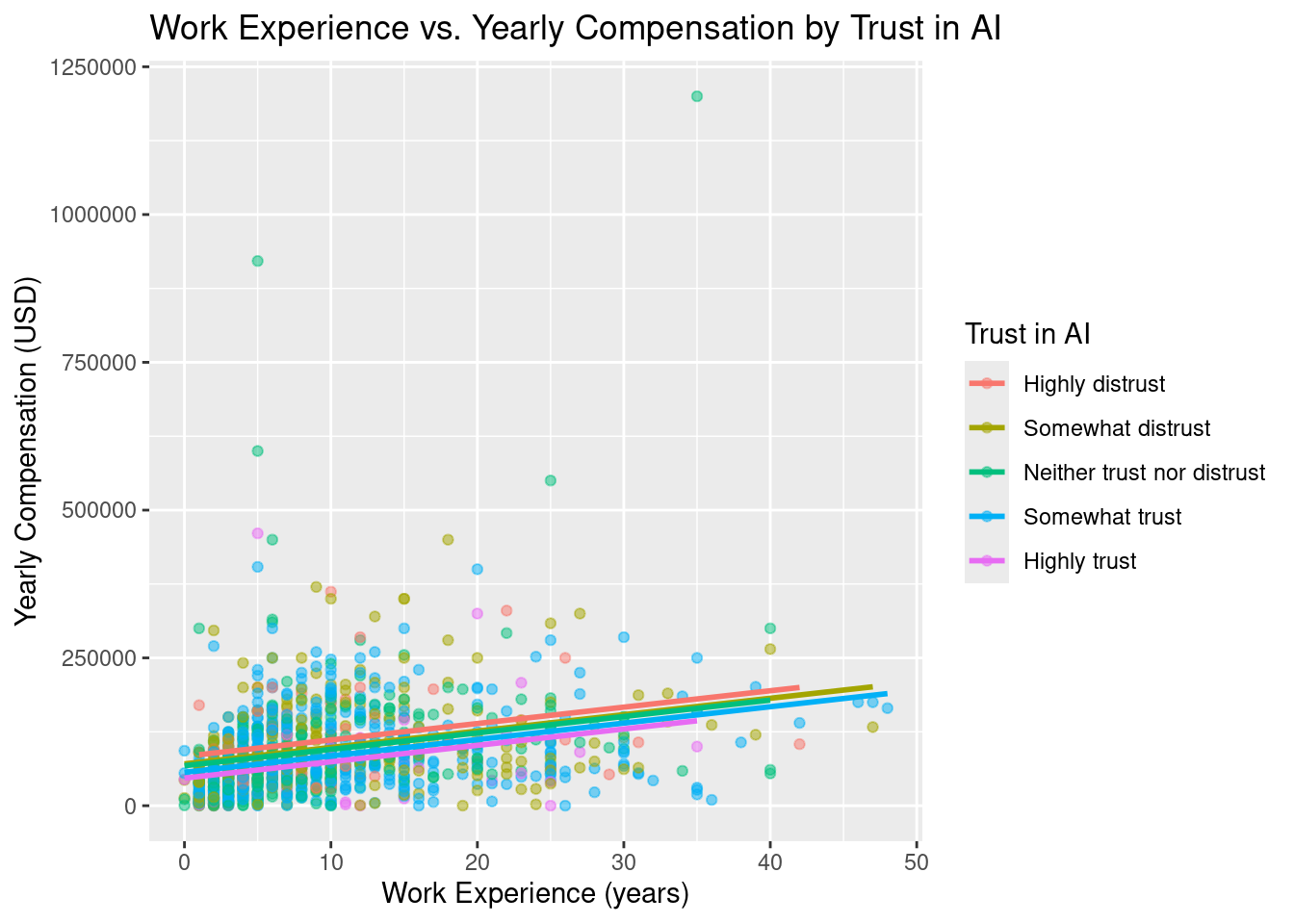
$ ai_trust <fct> Somewhat trust, Somewhat trust, Somewhat trust, Somewhat trust, Somewhat trust, Neither …